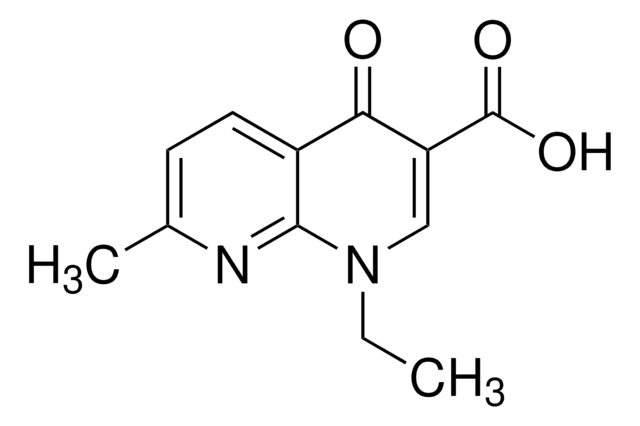
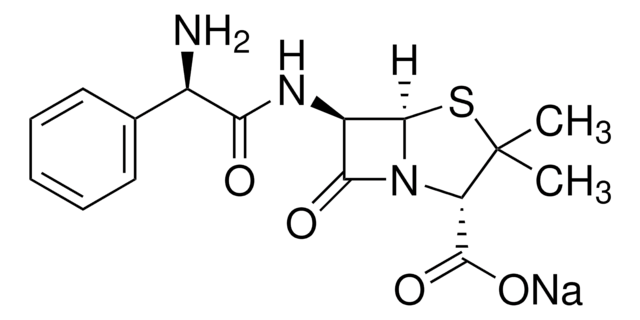
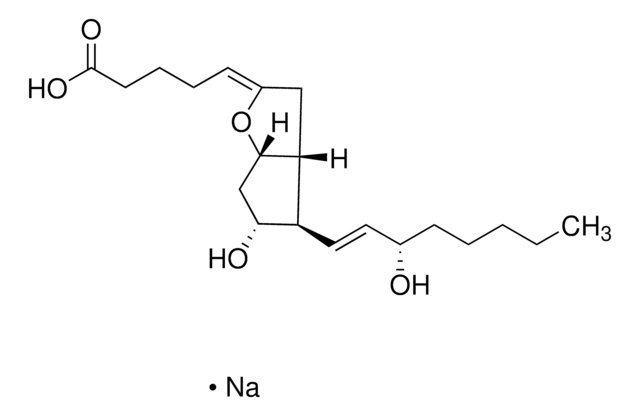
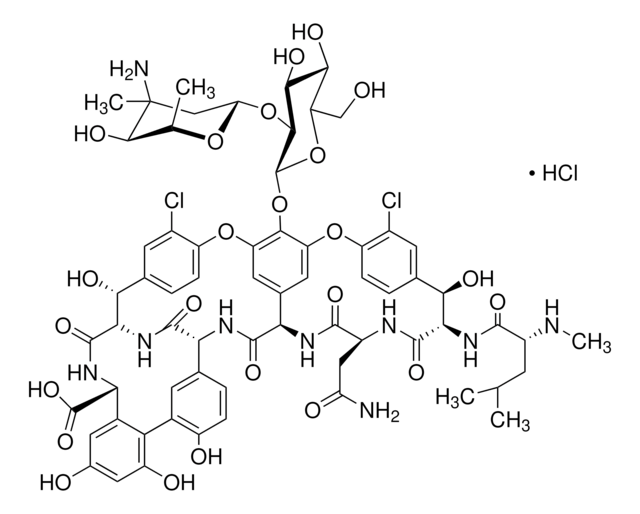
69550
Yeast Peptone 8 (powder)
suitable for microbiology, pH 6.5-7.5
Synonym(s):
Peptone from yeast No. 8, Peptone from yeast No. 8, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, ext.
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Quality Level
form
powder
shelf life
61 mo.
packaging
pkg of 500 g
storage condition
dry media (Tightly closed)
pH
6.5-7.5
solubility
water: soluble at 20 °C
application(s)
microbiology
components
(Total nitrogen ≥10.5Amino-N ≥3)
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | 1237600 | 1140666 | BP1061 |
|---|---|---|---|
| manufacturer/tradename BP | manufacturer/tradename USP | manufacturer/tradename USP | manufacturer/tradename BP |
| grade pharmaceutical primary standard | grade pharmaceutical primary standard | grade pharmaceutical primary standard | grade pharmaceutical primary standard |
| form solid | form - | form - | form solid |
| shelf life limited shelf life, expiry date on the label | shelf life - | shelf life - | shelf life limited shelf life, expiry date on the label |
| format neat | format neat | format neat | format neat |
| application(s) pharmaceutical | application(s) pharmaceutical (small molecule) | application(s) pharmaceutical (small molecule) | application(s) pharmaceutical |
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
- No animal-derived material
- Free of animal and human pathogens
- Free of allergens, pesticides, and GMO material
- No ethical or HALAL issues
- Greater batch consistency
- Greater flexibility thanks to modifiable specifications
- Lower CO2 footprint
- No need for import and export permits
Other Notes
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Apoptosis regulation involves multiple pathways and molecules for cellular homeostasis.
Cell cycle phases (G1, S, G2, M) regulate cell growth, DNA replication, and division in proliferating cells.
Related Content
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service