372838
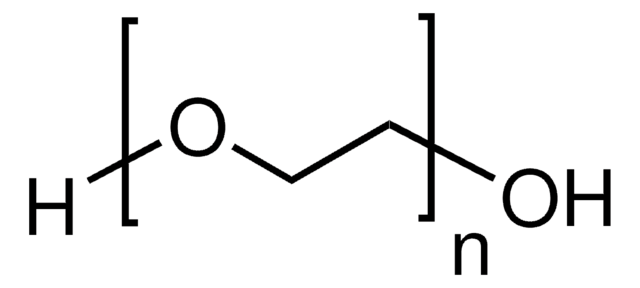
Poly(ethylene oxide)
average MV 8,000,000 (nominal), powder, hydroxyl, BHT as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
Polyethylene oxide, PEO
Select a Size
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Poly(ethylene oxide), average Mv ~8,000,000 (nominal), powder
form
powder
Quality Level
mol wt
average Mv ~8,000,000 (nominal)
contains
200-500 ppm BHT as inhibitor
viscosity
10,000-15,000 cP, 1 % in H2O(25 °C)
functional group
hydroxyl
SMILES string
[H]OCCO
InChI
1S/C2H6O2/c3-1-2-4/h3-4H,1-2H2
InChI key
LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | 189472 | 372803 | 189456 |
|---|---|---|---|
| functional group hydroxyl | functional group hydroxyl | functional group hydroxyl | functional group hydroxyl |
| form powder | form powder | form powder | form powder |
| Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 200 |
| mol wt average Mv ~8,000,000 (nominal) | mol wt average Mv ~5,000,000 (nominal) | mol wt average Mv ~2,000,000 (nominal) | mol wt average Mv ~900,000 (nominal) |
| contains 200-500 ppm BHT as inhibitor | contains 200-500 ppm BHT as inhibitor | contains 200-500 ppm BHT as inhibitor | contains 200-500 ppm BHT as inhibitor |
| viscosity 10,000-15,000 cP, 1 % in H2O(25 °C) | viscosity 5,500-7,500 cP, 1 % in H2O(25 °C, Brookfield)(lit.) | viscosity 2,000-4,000 cP, 2 % in H2O(25 °C, Brookfield)(lit.) | viscosity 8,800-17,600 cP, 5 % in H2O(25 °C, Brookfield)(lit.) |
Application
- Poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolyte for solid-state lithium batteries with high voltage positive electrodes: This study evaluates the role of electrolyte oxidation in battery performance, highlighting the challenges and potential improvements for PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes (Homann et al., 2020).
- Lithium bis (fluorosulfonyl) imide/poly (ethylene oxide) polymer electrolyte for all solid-state Li-S cell: Discusses the development of PEO-based polymer electrolytes for lithium-sulfur batteries, highlighting advances in energy storage technologies (Judez et al., 2017).
- Poly (ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries: Explores PEO-based materials as candidates for solid-state electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries, addressing challenges in electrical vehicle and portable electronics industries ( He, Xie, 2015).
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
281.5 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
138.6 °C - closed cup
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service