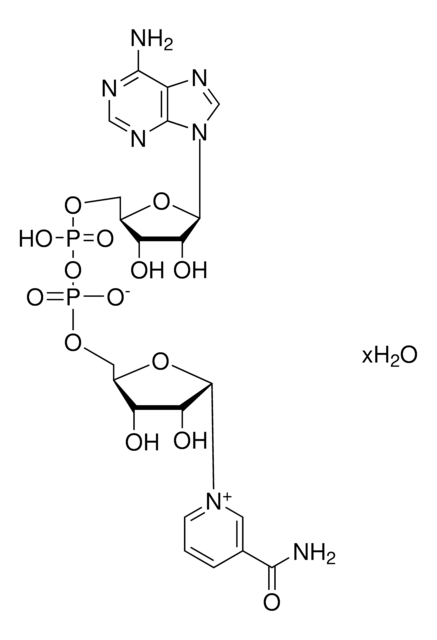
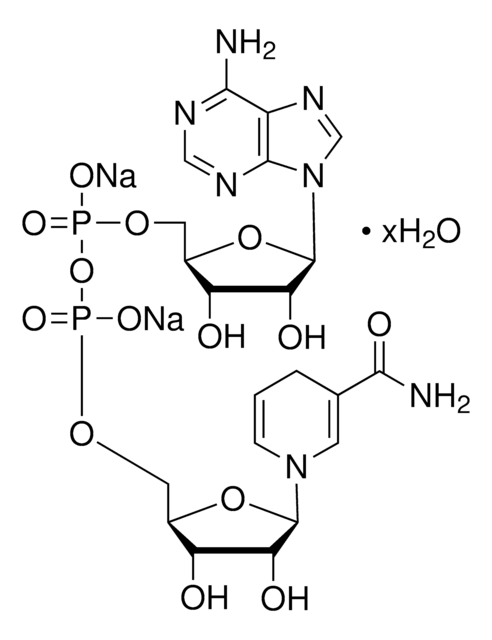
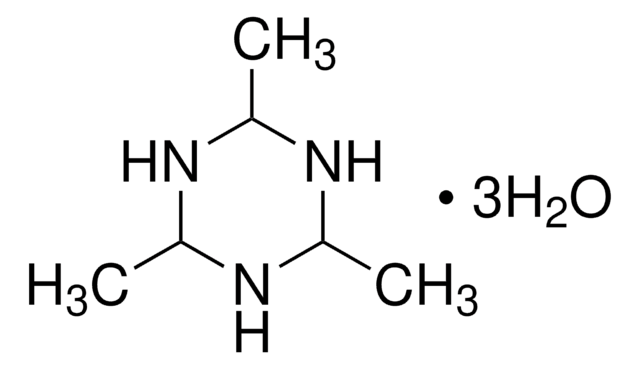
906662
QLAM-Iδ1TγLVproS-13CH3 Methyl Labeling Kit
About This Item
Recommended Products
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | 906654 | 906506 | 906646 |
|---|---|---|---|
| technique(s) bio NMR: suitable | technique(s) bio NMR: suitable | technique(s) bio NMR: suitable | technique(s) bio NMR: suitable |
| Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 |
| storage temp. −70°C | storage temp. −70°C | storage temp. −70°C | storage temp. −70°C |
| shipped in dry ice | shipped in dry ice | shipped in dry ice | shipped in dry ice |
General description
Application
Packaging
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Digoxigenin (DIG) labeling methods and kits for DNA and RNA DIG probes, random primed DNA labeling, nick translation labeling, 5’ and 3’ oligonucleotide end-labeling.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service