Cholesterol Oxidase Assay Procedure
Cholesterol oxidase from Streptomyces sp. has been used to assess the relationship between the micellar structure of model bile and the activity of esterase. Cholesterol oxidase has also been used to investigate the effects of sphingomyelin degradation on cell cholesterol oxidizability and steady-state distribution between the cell surface and the cell interior.
Native cholesterol oxidase (Product No. 228250) catalyzes oxidation of cholesterol to cholesterone and hydrogen peroxide (isoelectric points: 6.1 and 7.3). Cholesterol oxidase is suitable for determination of total cholesterol when coupled with cholinesterase and peroxidase.
Cholesterol Oxidase Assay Principle

The appearance of quinoneimine dye formed when coupled with 4-aminoantipyrine and phenol is measured at 500 nm by spectrophotometry.
Unit definition
One unit causes the formation of one micromole of hydrogen peroxide (half a micromole of quinoneimine dye) per minute under the conditions described below.
Reagents
| A. 0.1 M K-Phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 | |
| B. Cholesterol solution | To 5.0 mL of Triton X-100 on a hot plate or in a water bath, add 500 mg of cholesterol and mix with a stirring bar until cholesterol dissolves. Add 90 mL of distilled water to the hot cholesterol-Triton X-100 solution by slowly pouring along a stirring bar. Stir and allow to boil for 30 to 60 seconds. The solution will be cloudy. Cool under running water with gentle agitation, the solution will turn clear. Add 4.0 g of sodium cholate and dissolve. Fill up the solution to 100 mL with distilled water. This solution is stable for about one week at room temperature. If it becomes cloudy, warm slightly while stirring until it clears. |
| C. 4-AA solution | 1.76% (1.76 g 4-aminoantipyrine/100 mL of H2O) |
| D. Phenol solution | 6.0% (6.0 g phenol/100 mL of H2O) |
| E. POD solution | Horseradish peroxidase 15,000 purpurogallin units/100 mL of buffer (A) |
| F. Enzyme diluent | 20 mM K-Phosphate buffer, pH 7.0 contg. 0.2% bovine serum albumin |
Procedure
- Prepare the following working solution (20 tests volume), immediately before use and store on ice in a brown bottle.
51.0 mL Buffer solution (A)
4.0 mL Substrate solution (B)
1.0 mL 4-AA solution (C)
2.0 mL POD solution (E)
| Concentration in Assay Mixture | |
|---|---|
| K-Phosphate buffer | 87 mM |
| Cholesterol | 0.89 mM |
| 4-Aminoantipyrine | 1.4 mM |
| Phenol | 21 mM |
| Triton X-100 | 0.34 % |
| Sodium cholate | 64 mM |
| BSA | 33 μg/mL |
| POD | 5 U/mL |
- Pipette 2.9 mL of working solution into a cuvette (d=1.0 cm) and equilibrate at 37 ℃ for about 3 minutes. Add 0.1 mL of phenol solution (D), mix and keep at 37 ℃ for another 2 minutes.
- Add 0.1 mL of the enzyme solution* and mix with gentle inversion.
- Record the increase in optical density at 500 nm against water for 3 to 4 minutes in a spectrophotometer thermostated at 37 ℃, and calculate the ΔOD per minute from the linear portion of the curve (ΔOD test).
*At the same time, measure the blank rate (ΔOD blank) by using the same method as the test except that the enzyme diluent is added instead of the enzyme solution. Dissolve the enzyme preparation in ice-cold enzyme diluent (F), and dilute to 0.1-0.3 U/mL with the same buffer, and store on ice.
Calculation
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula:
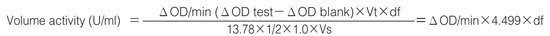
Weight activity (U/mg)=(U/mL)×1/C
| Vt | :Total volume (3.1 mL) |
| Vs | :Sample volume (0.1 mL) |
| 13.78 | :Millimolar extinction coefficient of quinoneimine dye under the assay conditions (F/micromole) |
| 1/2 | :Factor based on the fact that one mole of H2O2 produces half a mole of quinoneimine dye. |
| 1.0 | :Light path length (cm) |
| df | :Dilution factor |
| C | :Enzyme concentration in dissolution (c mg/mL) |
Materials
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?