284785
(S)-(+)-6-Methoxy-α-methyl-2-naphthaleneacetic acid
98%
Synonym(s):
Naproxen, (S)-(+)-2-(6-Methoxy-2-naphthyl)propionic acid
Select a Size
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
98%
optical activity
[α]25/D +66°, c = 1 in chloroform
mp
152-154 °C (lit.)
functional group
carboxylic acid
SMILES string
COc1ccc2cc(ccc2c1)[C@H](C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C14H14O3/c1-9(14(15)16)10-3-4-12-8-13(17-2)6-5-11(12)7-10/h3-9H,1-2H3,(H,15,16)/t9-/m0/s1
InChI key
CMWTZPSULFXXJA-VIFPVBQESA-N
Gene Information
human ... MAPK14(1432), PTGS1(5742), PTGS2(5743)
rat ... Alox5(25290), Ptgs1(24693)
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | SLW718242 | SLW718342 | SLW718234 |
|---|---|---|---|
| manufacturer/tradename 718247, SciLabware | manufacturer/tradename 718242, SciLabware | manufacturer/tradename 718342, SciLabware | manufacturer/tradename 718234, SciLabware |
| capacity 300 mL | capacity 120 mL | capacity - | capacity 100 mL |
| H 90 mm | H 75 mm | H - | H 60 mm |
| O.D. 120 mm | O.D. 100 mm | O.D. - | O.D. 80 mm |
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
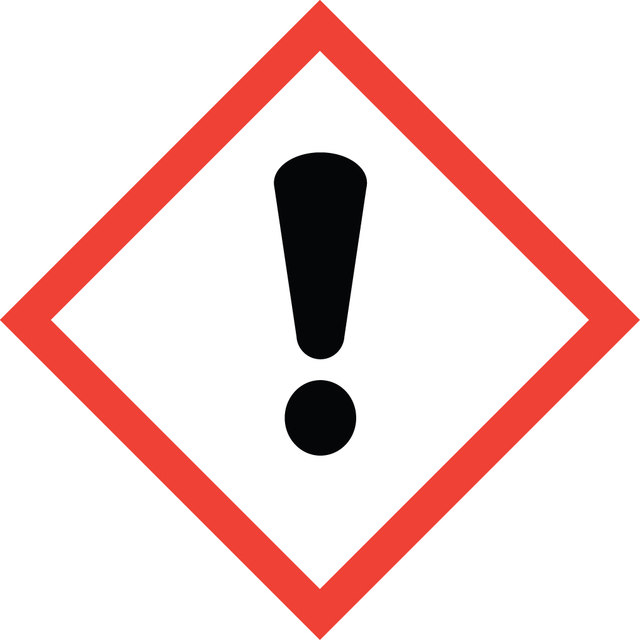
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
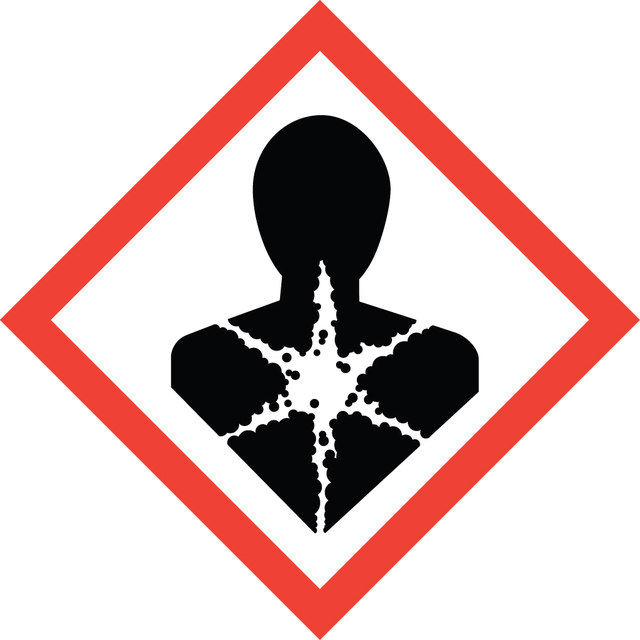
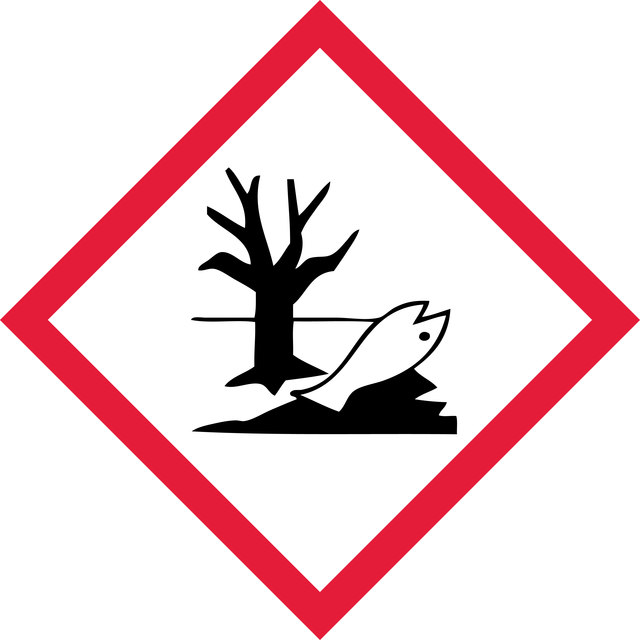
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service