HAWP09000
MCE Membrane Filter, 0.45 μm Pore Size
MF-Millipore™, filter diam. 90 mm, hydrophilic
Synonym(s):
Hydrophilic MCE membrane filter discs, Hydrophilic cellulose nitrate membrane filter discs, MF-Millipore™ Membrane Filter, 0.45 µm pore size, Mixed Cellulose Ester membrane filter discs
Select a Size
About This Item
₹52,360.00
Recommended Products
material
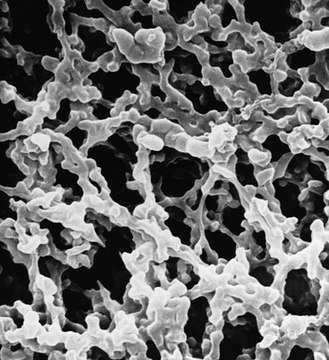
mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane
plain filter
white filter
Quality Level
description
90 mm diameter, mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, hydrophilic, white, 100 discs
sterility
non-sterile
feature
hydrophilic
manufacturer/tradename
MF-Millipore™
Millipore
parameter
4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate
60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate
75 °C max. temp.
diam.
90 mm
filter diam.
90 mm
thickness
150 μm
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
1 of 4
This Item | HAWP02500 | HAWP04700 | HAWP01300 |
|---|---|---|---|
| material mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, white filter, plain filter | material mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, plain filter, white filter | material mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, plain filter, white filter | material mixed cellulose esters (MCE) membrane, plain filter, white filter |
| manufacturer/tradename MF-Millipore™ | manufacturer/tradename MF-Millipore™ | manufacturer/tradename MF-Millipore™ | manufacturer/tradename MF-Millipore™ |
| parameter 60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate, 4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate, 75 °C max. temp. | parameter 4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate, 60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate, 75 °C max. temp. | parameter 4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate, 60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate, 75 °C max. temp. | parameter 4 L/min-cm2 air flow rate, 60 mL/min-cm2 water flow rate, 75 °C max. temp. |
| pore size 0.45 μm pore size, 79 % porosity | pore size 0.45 μm pore size, 79 % porosity | pore size 0.45 μm pore size, 79 % porosity | pore size 0.45 μm pore size, 79 % porosity |
| sterility non-sterile | sterility non-sterile | sterility non-sterile | sterility non-sterile |
| feature hydrophilic | feature hydrophilic | feature hydrophilic | feature hydrophilic |
General description
MF-Millipore filters without Triton surfactant contain minimum amounts of wetting agent and have a lower water extractable content than standard MF-Millipore filters.
Features & Benefits:
- Versatile filter for biological and environmental monitoring applications
- Available in a range of pore sizes, colored black or white, with or without a gridded surface
- Compatible with ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation, and autoclave sterilization methods
Application
- Clarification of aqueous solutions
- Particle removal
- Particle analysis
- Microbiology analysis
- Isolation of virus-like particles in wastewater
- Microplastics analysis grade water
- Nucleic acid binding, including eDNA
Other Notes
- Organism Retention: Microorganism
- Mode of Action: Filtration (size exclusion)
- Application: General laboratory filtration
- Intended Use: Retention or removal of biological contaminants
- Instructions for Use: Sterilizing filtration of a liquid through a membrane with a 0.2 μm (or smaller) pore size effectively removes biological contaminants, including bacteria, mold and yeast. For the selective retention of larger biological contaminents, liquid filtration through membranes with 0.45 μm (or larger) pore sizes may be used to trap and support microorganism growth for subsequent culture and analysis
- Storage Statement: Store in dry location away from heat source
- Disposal Statement: Dispose of in accordance with applicable federal, state and local regulations.
Legal Information
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Flam. Sol. 1
Storage Class Code
4.1B - Flammable solid hazardous materials
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service