C3144
Coenzyme A sodium salt hydrate
cofactor for acyl transfer
Synonym(s):
CoA Na2
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(5)
About This Item
Empirical Formula (Hill Notation):
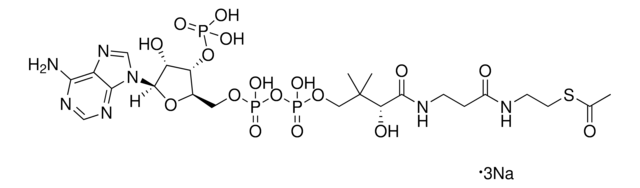
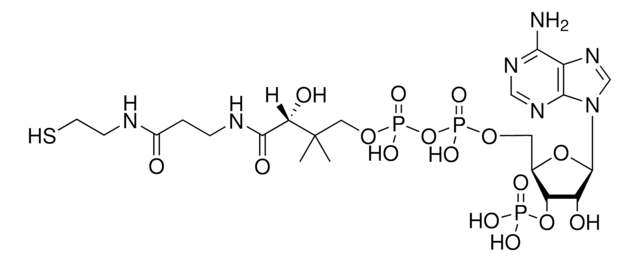
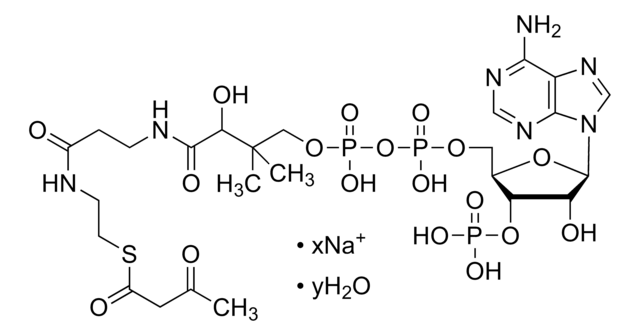
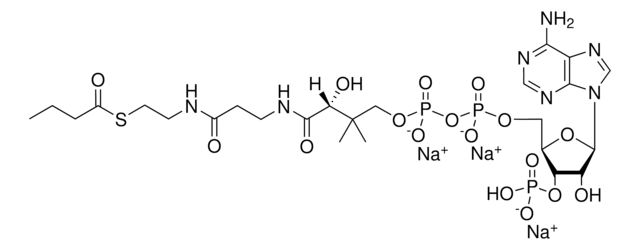
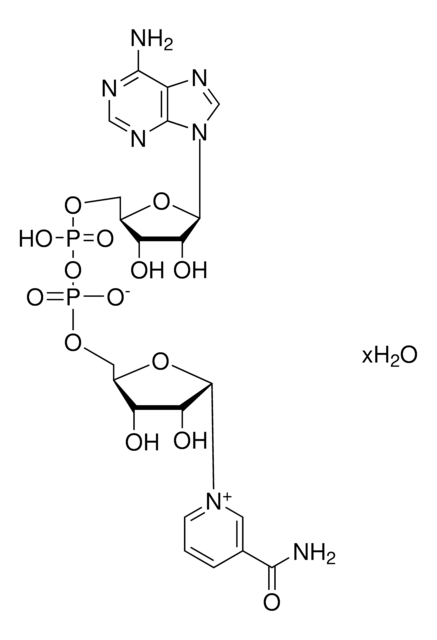
C21H36N7O16P3S · xNa+ · yH2O
CAS Number:
Molecular Weight:
767.53 (anhydrous free acid basis)
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
41106305
PubChem Substance ID:
NACRES:
NA.51
Recommended Products
description
cofactor for acyl transfer
Quality Level
Assay
≥85% (spectrophotometric assay)
form
powder
solubility
H2O: soluble 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
storage temp.
−20°C
SMILES string
[Na+].CC(C)(COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OC[C@H]1O[C@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1OP(O)([O-])=O)n2cnc3c(N)ncnc23)C(O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCS
InChI key
SYTRWOCXZXQBPW-CLVRNSBASA-M
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Coenzyme A (CoA) is an essential cofactor in living systems and is synthesized from pantothenic acid (vitamin B5), The CoA levels in mitochondria and peroxisomes correspond to 2-5 mM and 0.7 mM, respectively. Cytosolic CoA is in the range of 0.05 mM to 0.14 mM
Application
Coenzyme A is suitable for use in:
- gylcerolipid biosynthesis in porcine adipose tissue
- an assay to measure the level of Alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) in human blood samples using a nanoparticle electrochemical biosensor
- chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) assay
- the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, which is required for palmitoylation and activation of proteins for regulated membrane fusion
Biochem/physiol Actions
Coenzyme A (CoA, CoASH, HSCoA) is a coenzyme that facilitates enzymatic acyl-group transfer reactions and supports the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids. CoA is involved in the mechanisms of a wide variety of enzymes. In the presence of CoASH, organic carboxylic acids form acyl-CoA thioesters, which facilitates enzyme recognition. The acyl-CoA formed from xenobiotic carboxylic acids can add to the compound′s toxicity, which can lead to cellular metabolic dysfunction. It is involved in the oxidation of pyruvate in the Kreb′s cycle. CoA is needed for metabolic events. The bacterial CoA pathway is targeted for antimicrobial development. It mediates acyl group transfer and carbonyl activation. The CoA and its thioester levels are crucial for cellular homeostasis. CoA is also involved in regulating platelet aggregation and vasoconstriction. It acts as an essential cofactor in enzymatic acetyl transfer reactions.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service