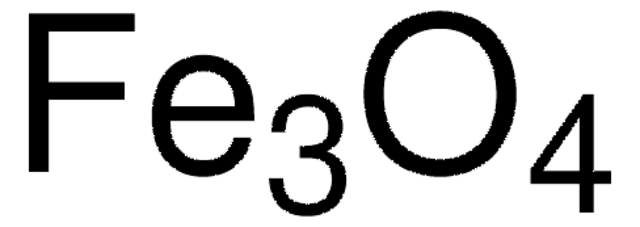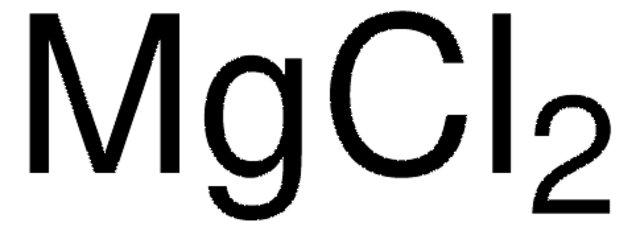12310
Iron
≥99%, reduced, powder (fine)
Synonyme(s) :
Fe
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Essai
≥99%
Forme
powder (fine)
Qualité
reduced
Pertinence de la réaction
core: iron
reagent type: catalyst
Résistivité
9.71 μΩ-cm
Impuretés
≤0.5% insoluble in HCl
pb
2750 °C (lit.)
Pf
1535 °C (lit.)
Densité
7.86 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
Traces d'anions
chloride (Cl-): ≤20 mg/kg
sulfide (S2-): ≤100 mg/kg
Traces de cations
As: ≤5 mg/kg
Cu: ≤100 mg/kg
Mn: ≤1000 mg/kg
Ni: ≤500 mg/kg
Pb: ≤20 mg/kg
Zn: ≤50 mg/kg
Chaîne SMILES
[Fe]
InChI
1S/Fe
Clé InChI
XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
In chemical synthesis, reduced iron powder can be employed as a reducing agent, catalyst, or precursor in a wide range of reactions. It is commonly used to convert organic functional groups, such as aldehydes, ketones, and nitro compounds, into their corresponding reduced forms. It is also known to facilitate hydrogenation reactions.
Reduced iron powder finds applications in the production of iron-based catalysts, magnetic materials, pigments, and metal alloys. It is commonly used in pharmaceutical synthesis, organic chemistry, and industrial manufacturing. It is important to handle reduced iron powder with care due to its potential reactivity with moisture and oxygen, which may cause oxidation and result in changes to its properties. Proper storage and handling procedures should be followed to maintain its quality and prevent unwanted reactions.
Application
- Sodium-Ion Batteries: Research demonstrated the use of iron-based Na(4)FeV(PO(4))(3) nanoparticles in pine pollen derived carbon matrices as a cost-effective cathode for sodium-ion batteries, emphasizing sustainable energy solutions and materials chemistry (Wang et al., 2024).
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Flam. Sol. 1 - Self-heat. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
4.2 - Pyrophoric and self-heating hazardous materials
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
nwg
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique