809470
Lithium hexafluorophosphate solution
in propylene carbonate, 2.0 M LiPF6 PC, battery grade
Synonym(s):
2M LiPF6 PC
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
battery grade
Quality Level
form
solution
greener alternative product characteristics
Design for Energy Efficiency
Learn more about the Principles of Green Chemistry.
sustainability
Greener Alternative Product
concentration
2.0 M (LiPF6 in PC)
impurities
≤15 ppm H2O
≤50 ppm HF
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤1 ppm
sulfate (SO42-): ≤2 ppm
cation traces
Ca: ≤1 ppm
Fe: ≤1 ppm
K: ≤1 ppm
Na: ≤1 ppm
Pb: ≤1 ppm
application(s)
battery manufacturing
greener alternative category
SMILES string
F[P-](F)(F)(F)(F)F.[Li+]
InChI
1S/F6P.Li/c1-7(2,3,4,5)6;/q-1;+1
InChI key
AXPLOJNSKRXQPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
- H2O <15 ppm
- HF <50 ppm
- APHA <50
- Battery grade
Application
Other Notes
Legal Information
1 of 4
This Item | 809403 | 809357 | 746789 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 100 |
| grade battery grade | grade battery grade | grade battery grade | grade battery grade |
| concentration 2.0 M (LiPF6 in PC) | concentration 2.0 M (LiPF6 in ETC) | concentration (2.0 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC) | concentration (1.0 M LiPF6 in PC) |
| form solution | form solution | form liquid | form solution |
| application(s) battery manufacturing | application(s) battery manufacturing | application(s) battery manufacturing | application(s) battery manufacturing |
| impurities ≤15 ppm H2O, ≤50 ppm HF | impurities ≤15 ppm H2O, ≤50 ppm HF | impurities ≤15 ppm H2O, ≤50 ppm HF | impurities <15 ppm H2O, <50 ppm HF |
Still not finding the right product?
Explore all of our products under Lithium hexafluorophosphate solution
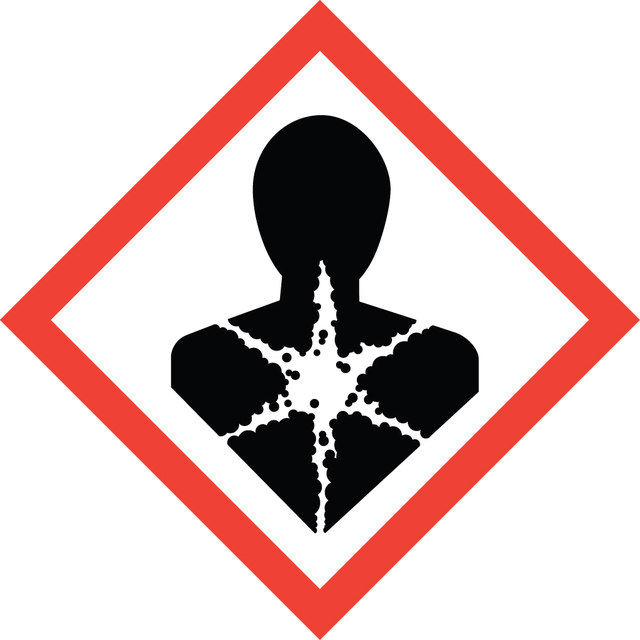
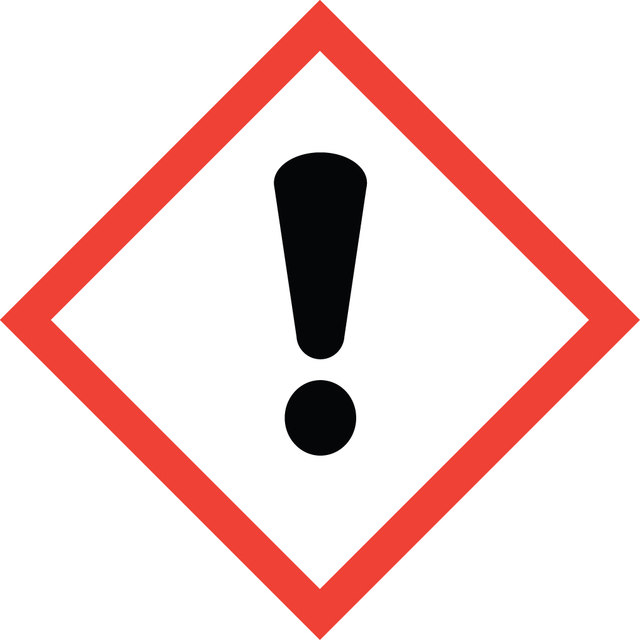
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 1 Inhalation
Target Organs
Bone,Teeth
Storage Class Code
6.1D - Non-combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic hazardous materials or hazardous materials causing chronic effects
WGK
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Don't see the Right Version?
If you require a particular version, you can look up a specific certificate by the Lot or Batch number.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Articles
Due to the adverse impact of the continued use of fossil fuels on the earth’s environment and climate, researchers have been asked to develop new approaches for producing power using renewable sources like wind and solar energy
Ionic Liquids Based Electrolytes for Rechargeable Batteries