T7539
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α from mouse
≥95%, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, powder, suitable for cell culture
Synonym(s):
mTNF-α, TNF-α
About This Item
Recommended Products
Product Name
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α from mouse, TNF-α, recombinant, expressed in E. coli, powder, suitable for cell culture
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Assay
≥95%
form
powder
potency
0.01-0.5 ng/mL EC50
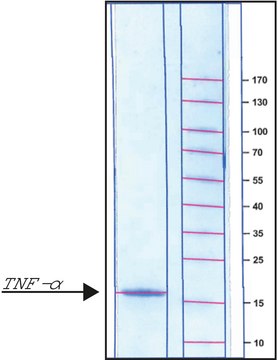
mol wt
17 kDa
packaging
pkg of 10 μg
pkg of 50 μg
storage condition
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
Related Categories
1 of 4
This Item | T7799 | T5944 | T6674 |
|---|---|---|---|
| technique(s) cell culture | mammalian: suitable | technique(s) cell culture | mammalian: suitable | technique(s) cell culture | mammalian: suitable | technique(s) cell culture | mammalian: suitable |
| recombinant expressed in E. coli | recombinant expressed in E. coli | recombinant expressed in E. coli | recombinant expressed in E. coli |
| biological source mouse | biological source human | biological source rat | biological source human |
| assay ≥95% | assay >95% (SDS-PAGE) | assay ≥98% (SDS-PAGE and HPLC) | assay ≥97% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 200 |
| form powder | form powder | form powder | form powder |
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Unit Definition
Physical form
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Lipid Induced Insulin Resistance
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service