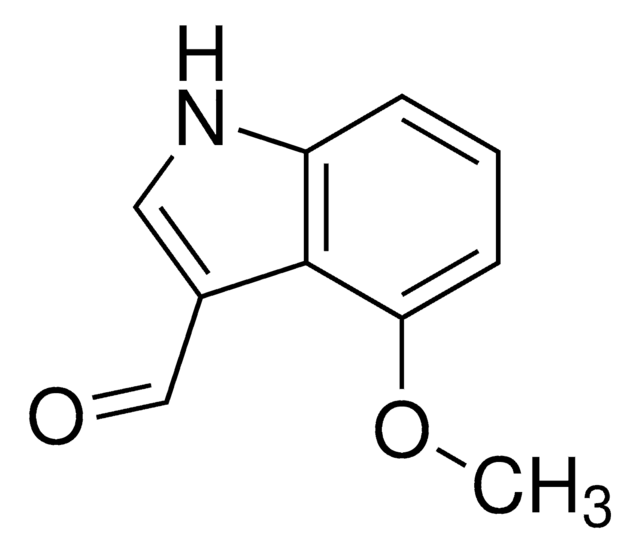
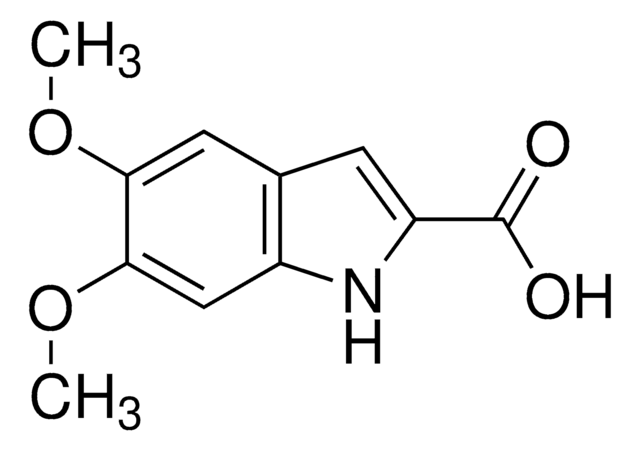
50702-U
Ascentis® Express 90 Å PCS-Phenyl-Hexyl, 2.7 µm HPLC Column
column L × I.D. 150 mm × 4.6 mm, pk of 1 ea
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41115709
NACRES:
SB.52
Pricing and availability is not currently available.
Recommended Products
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
1 of 4
This Item | CDS004557 | CDS000930 | M14951 |
|---|---|---|---|
| form solid | form solid | form solid | form - |
General description
Ascentis® Express PCS-Phenyl-Hexyl columns are specifically engineered to provide efficient separation of basic, acidic, or neutral compounds under low ionic strength (formic acid) mobile phase conditions. These columns contain advanced Fused-Core® particles with pores strategically sized to 90 Å for small molecule analyses. This attribute makes these columns an excellent choice for pharmaceutical method development. The unique PCS-C18 chemistry enables exceptional peak shape and enhanced loading capacity of basic compounds as compared to traditional C18 chemistries. This column also provides orthogonal selectivity to other small molecule chemistries.
Analysis Note
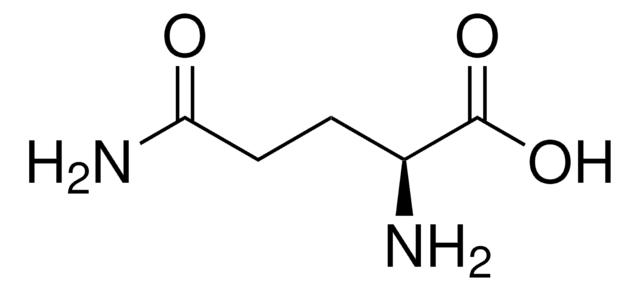
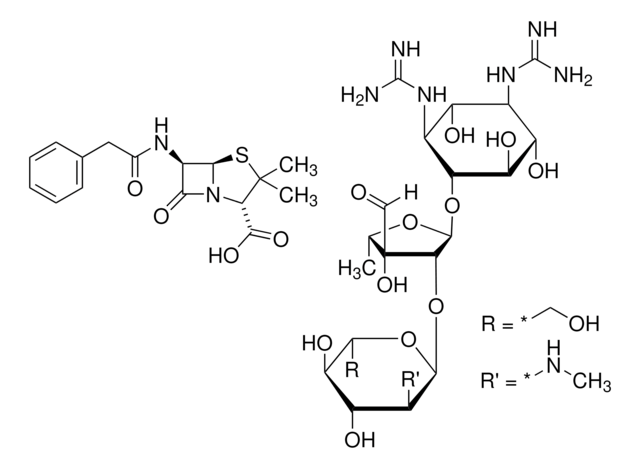
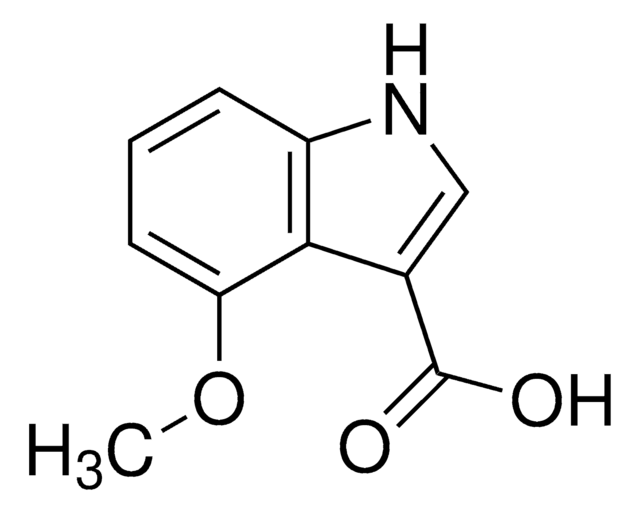
The target analytes include basic compounds.
Legal Information
Ascentis is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Fused-Core is a registered trademark of Advanced Materials Technology, Inc.
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
C Mignon et al.
Scientific reports, 7(1), 2797-2797 (2017-06-07)
Photobiomodulation-based (LLLT) therapies show tantalizing promise for treatment of skin diseases. Confidence in this approach is blighted however by lamentable inconsistency in published experimental designs, and so complicates interpretation. Here we interrogate the appropriateness of a range of previously-reported treatment
Giuseppe Antonacci et al.
Scientific reports, 6, 37217-37217 (2016-11-16)
Cellular biomechanics play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of several diseases. Unfortunately, current methods to measure biomechanical properties are invasive and mostly limited to the surface of a cell. As a result, the mechanical behaviour of subcellular structures and
Kenji Ohe et al.
The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology, 182, 21-26 (2018-04-22)
The high-mobility group A protein 1a (HMGA1a) protein is known as an oncogene whose expression level in cancer tissue correlates with the malignant potential, and known as a component of senescence-related structures connecting it to tumor suppressor networks in fibroblasts.
Fabian E Ortega et al.
eLife, 8 (2019-02-06)
Listeria monocytogenes hijacks host actin to promote its intracellular motility and intercellular spread. While L. monocytogenes virulence hinges on cell-to-cell spread, little is known about the dynamics of bacterial spread in epithelia at a population level. Here, we use live
Xin Gu et al.
Analytical chemistry, 88(14), 7191-7197 (2016-06-30)
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is known as a key molecule in a variety of biological processes, as well as a crucial byproduct in many enzymatic reactions. Therefore, being able to selectively and sensitively detect H2O2 is not only important in monitoring
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service