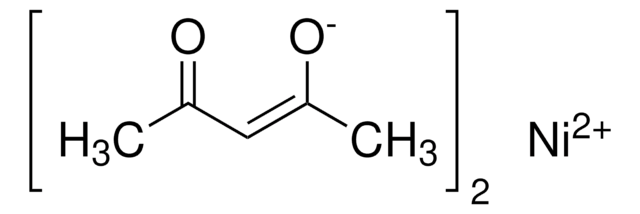
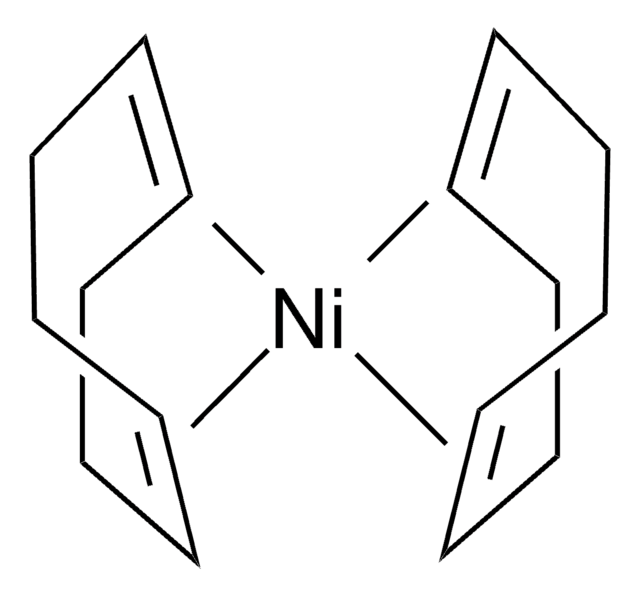
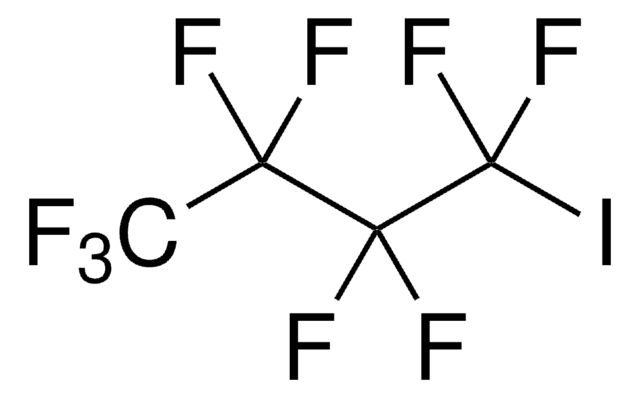
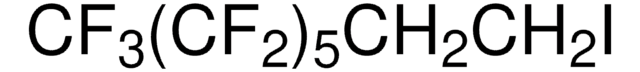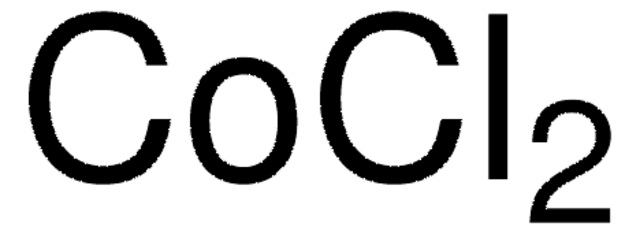일반 설명
Nickel(II) chloride anhydrous, powder, 99.99% trace metals basis comes in a powder form or in chunks with trace metal impurities ≤ 150.0 ppm. It is a highly useful inorganic compound with a broad range of applications across various industries. Its relatively high purity makes it suitable for both industrial and laboratory settings. It is widely used in catalysis, electroplating, battery manufacturing, chemical synthesis, material science, dye and pigment production, and laboratory research.
애플리케이션
Nickel(II) chloride anhydrous can be used in advanced studies in battery technologies, such as nickel-based cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries and alternative battery chemistries. Used to investigate and improve the properties of electrode materials in nickel-cadmium (NiCd) and nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries. Research into electrocatalysts for energy applications, including water splitting and fuel cells, frequently utilizes high-purity Nickel(II) chloride to ensure optimal performance and reproducibility. It can be used as a precursor in the synthesis of nickel nanoparticles, which have applications in catalysis, magnetic materials, and electronic devices. The high purity Nickel(II) chloride serves as a precursor for various nickel compounds, such as nickel oxides and hydroxides, which are studied for their electrical, magnetic, and catalytic properties.
특징 및 장점
Its high purity guarantees accurate and reproducible experimental results, making it essential for applications in catalysis, nanomaterial synthesis, battery research, material science, coordination chemistry, environmental chemistry, and analytical chemistry. The vapor-phase co-reductions with other metal halides such as aluminum chloride (cat. no. 449598) by hydrogen results in finely divided intermetallics with applications as structural materials or compounds with useful thermoelectric, magnetic, and oxidation-resistance properties. Used in the synthesis of semiconducting metal-containing polymers in which the polypyrrole backbone has a conformational energy minimum and is nearly planar.
The vapor-phase co-reductions with other metal halides such as aluminum chloride (cat. no. 449598) by hydrogen results in finely divided intermetallics with applications as structural materials or compounds with useful thermoelectric, magnetic, and oxidation-resistance properties. Used in the synthesis of semiconducting metal-containing polymers in which the polypyrrole backbone has a conformational energy minimum and is nearly planar.