SML1822
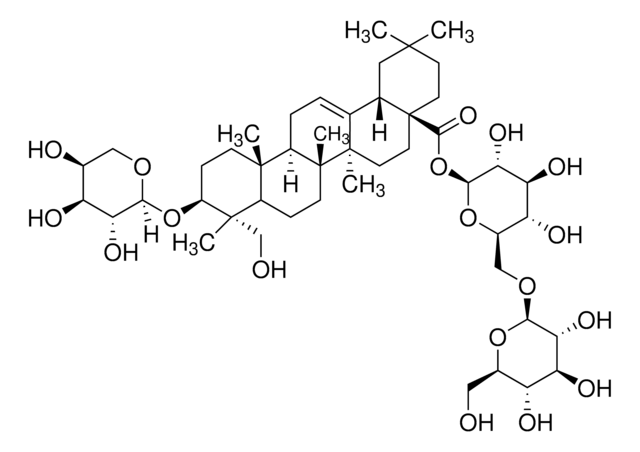
Akebia saponin D
≥98% (HPLC)
동의어(들):
3-O-α-L-arabinopyranosyl hederagenin-28-β-D-glucopyranoside-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside, ASD, Asperosaponin VI, Leiyemudanoside A, Tauroside St-G0-1
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
크기 선택
보기 변경
1 G
MYR 1,625.00
About This Item
MYR 1,625.00
장바구니에서 구매 가능 여부 확인하기
추천 제품
1 of 4
이 품목 | SMB00424 | 53889 | 1048233 |
|---|---|---|---|
| form powder | form powder | form - | form - |
| assay ≥98% (HPLC) | assay ≥98% (HPLC) | assay ≥95% (HPLC) | assay - |
| Quality Level 100 | Quality Level 200 | Quality Level 100 | Quality Level - |
| storage temp. −20°C | storage temp. 2-8°C | storage temp. - | storage temp. 2-8°C |
| solubility H2O: 3 mg/mL, clear (warmed) | solubility - | solubility - | solubility - |
| storage condition desiccated | storage condition - | storage condition - | storage condition - |
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Akebia saponin D (ASD) is a bioactive triterpenoid saponin isolated from the rhizome of Dipsacus asper Wall that is used as an anti-osteoporosis drug.
Akebia saponin D (ASD) is a bioactive triterpenoid saponin isolated from the rhizome of Dipsacus asper Wall that is used as an anti-osteoporosis drug. Akebia saponin D exhibits therapeutic effects in number of disease models including cancer, Alzheimer′s disease, cardiovascular disease, and bone fractures. Akebia saponin D protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) liver damage in mice model of NAFLD. ASD decreases hepatic steatosis and heptocyte apoptosis through autophagy modulation. Akebia saponin D prevents oleic acid induced lipid droplets accumulation and increases autophagic flux BRL cells.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
Not applicable
Flash Point (°C)
Not applicable
가장 최신 버전 중 하나를 선택하세요:
이미 열람한 고객
Keith C Meyer et al.
The European respiratory journal, 44(6), 1479-1503 (2014-11-02)
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) is a major complication of lung transplantation that is associated with poor survival. The International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation, American Thoracic Society, and European Respiratory Society convened a committee of international experts to describe
Sarah E Burr et al.
Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 92(7), 490-498 (2014-08-12)
To evaluate the effect of repeated mass drug administration (MDA) of azithromycin in the Gambia on the nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae and on the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains. This study involved villages that participated in a cluster randomized trial
Katharina Krenn et al.
The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery, 149(4), 1194-1202 (2015-01-18)
Azithromycin has become a standard of care in therapy of bronchiolitis obliterans following lung transplantation. Matrix metalloprotease-9 broncho-alveolar lavage levels increase in airway neutrophilia and bronchiolitis obliterans. Interleukin-17 may play a role in lung allograft rejection, and interleukin-12 is downregulated
Alison M Binder et al.
American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine, 188(7), 807-812 (2013-08-10)
Persons with cystic fibrosis (CF) are at high risk of nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) infection, with treatment requiring prolonged multidrug regimens that include macrolides. Although macrolides, specifically azithromycin, are used in the management of patients with CF with chronic Pseudomonas, macrolide-resistant
Josje Altenburg et al.
JAMA, 309(12), 1251-1259 (2013-03-28)
Macrolide antibiotics have been shown beneficial in cystic fibrosis (CF) and diffuse panbronchiolitis, and earlier findings also suggest a benefit in non-CF bronchiectasis. To determine the efficacy of macrolide maintenance treatment for adults with non-CF bronchiectasis. The BAT (Bronchiectasis and
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.