Attachment Factors
Mammalian cells grow within a complex mixture of extracellular polymers and signaling molecules in vivo. This mixture is called the extracellular matrix (ECM) and interactions between it and the cell are critical for physiological processes including cellular growth and differentiation, formation of morphological features, and cell motility. Some cells cultured in vitro have the capacity to readily express and secrete the components of the ECM when grown on glass or polystyrene culturing chambers. Other cell types do not readily produce ECM components and can therefore be challenging to culture when they do not adhere to the culture surface, limiting their capacity for predictive modeling of physiological processes. One solution is to coat cultureware with components of the ECM, or with synthetic polymers that otherwise mimic the interactions between a cell and the ECM. These components are referred to as attachment factors, and they can be a critical component of culturing healthy and viable cells in vitro. test2304
Products
Essential Attachment Factors
Numerous natural and synthetic attachment factors have been developed for use in cell culture applications. In some cases, attachment factors must be tested empirically for suitability for a given cell culturing condition. Below is a list of common attachment factors for consideration when optimizing cell culture conditions.
|
|
|
Choosing Attachment Factors
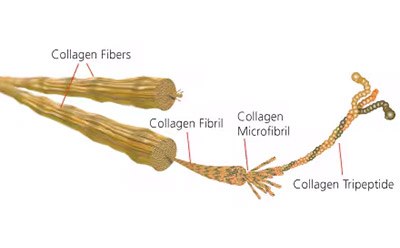
Many of these attachment factors are derived from different biological sources, and occur as multiple isoforms. Some attachment factors are purely synthetic, like Poly-L-Lysine. In certain applications, a peptide fragment of a factor (such as collagen) can be a useful alternative to the full-length protein. For convenience in cell culture applications, many attachment factors can be purchased in a liquid format that facilitates coating cultureware; for even greater efficiency, culture surfaces precoated with attachment factors save time and increase reproducibility.
Related Product Resources
- Article: Extracellular Matrix Proteins and Tools for Cell Culture Optimization
Białka macierzy zewnątrzkomórkowej, takie jak laminina, kolagen i fibronektyna, mogą być stosowane jako podłoża do mocowania komórek w hodowli komórkowej.
- Article: Fibronectin
Fibronektyna (FN) odgrywa kluczową rolę w tworzeniu fibryli macierzy zewnątrzkomórkowej i interakcjach komórkowych.
- Protocol: Poly-L-Lysine Cell Attachment
Przyleganie komórek do stałych podłoży za pomocą poli-lizyny, która wzmacnia elektrostatyczne oddziaływanie między ujemnie naładowanymi jonami błony komórkowej a powierzchnią hodowli.
- Protocol: Laminin Coating for Cell Culture
Coating surfaces with laminin for culturing cells requires specific conditions for optimal results. Protocols for coating coverslips to culture neurospheres and general cell culture are included.
Zaloguj się lub utwórz konto, aby kontynuować.
Nie masz konta użytkownika?