About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
233 hPa ( 20 °C)
Quality Level
form
liquid
reaction suitability
reagent type: oxidant
kinematic viscosity
0.314 cSt(20 °C)
bp
58.8 °C/1013 hPa
mp
-7.3 °C
solubility
35 g/L
density
3.12 g/cm3 at 20 °C (liquid)
storage temp.
15-25°C
SMILES string
[Br-]
InChI
1S/BrH/h1H/p-1
InChI key
CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M
Related Categories
General description
Application
- Primary alcohols to either aldehydes or esters and secondary alcohols to give ketones.
- Alcohols or diols to tetrahydrofurans in the presence of silver(I) salts.
- Enediol bis-trimethylsilyl ethers to α-diketones.
- Aldehydes to esters in the presence of alcohol solvents and sodium bicarbonate buffer.
- Aliphatic and aromatic thiols to disulfides.
Bromine can also be used along with other co-reactants such as hexamethylphosphoric triamide (HMPA) and bis(tributyltin) oxide (HBD) to selectively oxidize secondary alcohols. However, bromine/nickel carboxylates convert 1,4-diols to γ-butyrolactones by selective oxidation of the primary alcohols.
Analysis Note
signalword
Danger
hcodes
Hazard Classifications
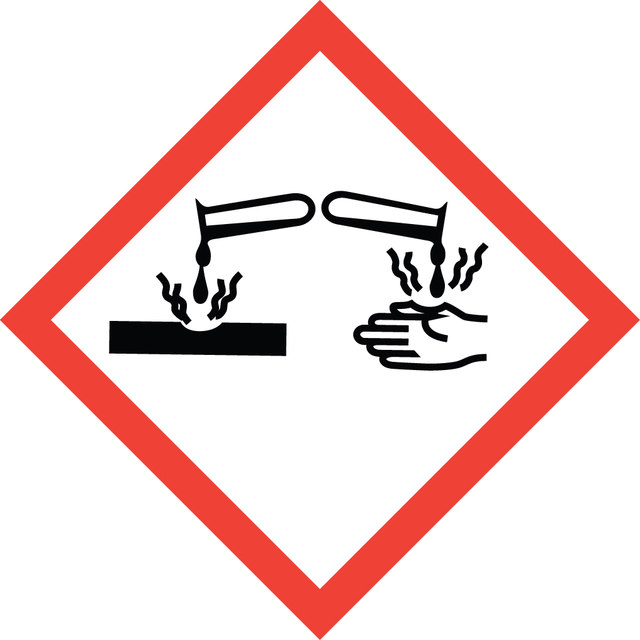
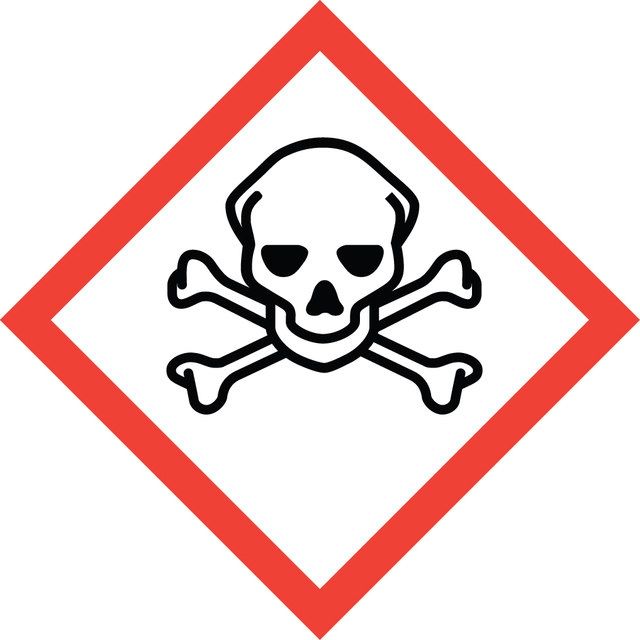
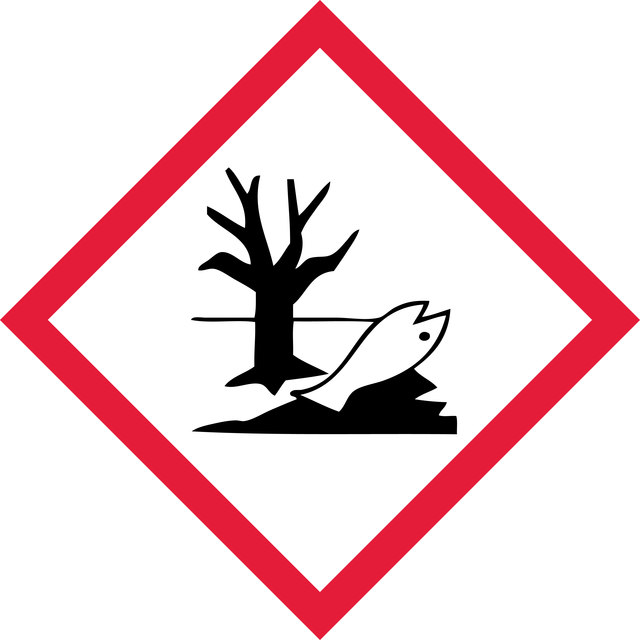
Acute Tox. 1 Inhalation - Aquatic Acute 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Corr. 1A
Storage Class
6.1B - Non-combustible, acute toxic Cat. 1 and 2 / very toxic hazardous materials
wgk_germany
WGK 2
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service