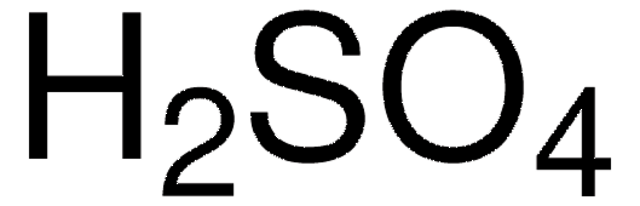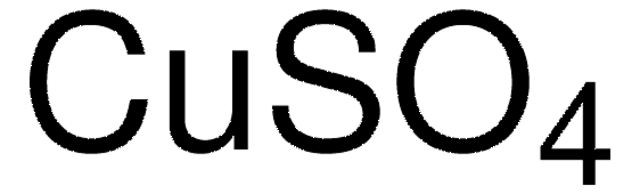12849
Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
puriss., suitable for, meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur., BP, USP,FCC
Synonym(s):
Cupric sulfate pentahydrate, Sulfuric acid, copper(II) salt (1:1) pentahydrate
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor pressure
7.3 mmHg ( 25 °C)
Quality Level
grade
puriss.
assay
98.5-100.5% (USP)
form
crystals
quality
meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur., BP, USP,FCC
loss
35.0-36.5% loss on drying, 250 °C
pH
3.5-4.5 (20 °C, 50 g/L)
mp
110 °C (dec.) (lit.)
anion traces
chloride (Cl-): ≤100 mg/kg
cation traces
As: ≤5 mg/kg
Ca: ≤50 mg/kg
Fe: ≤30 mg/kg
K: ≤100 mg/kg
Mg: ≤50 mg/kg
Na: ≤200 mg/kg
Ni: ≤50 mg/kg
Pb: 4 ppm
suitability
passes test for appearance of solution
suitable for
SMILES string
O.O.O.O.O.[Cu++].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O
InChI
1S/Cu.H2O4S.5H2O/c;1-5(2,3)4;;;;;/h;(H2,1,2,3,4);5*1H2/q+2;;;;;;/p-2
InChI key
JZCCFEFSEZPSOG-UHFFFAOYSA-L
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
- As catalyst for the acetylation of alcohols and phenols under solvent-free conditions.
- To compose the electrolyte for the electrodeposition of Cu-Zn-Sn precursors, required for the preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films.
- As catalyst for the dehydration of alcohols.
signalword
Danger
hcodes
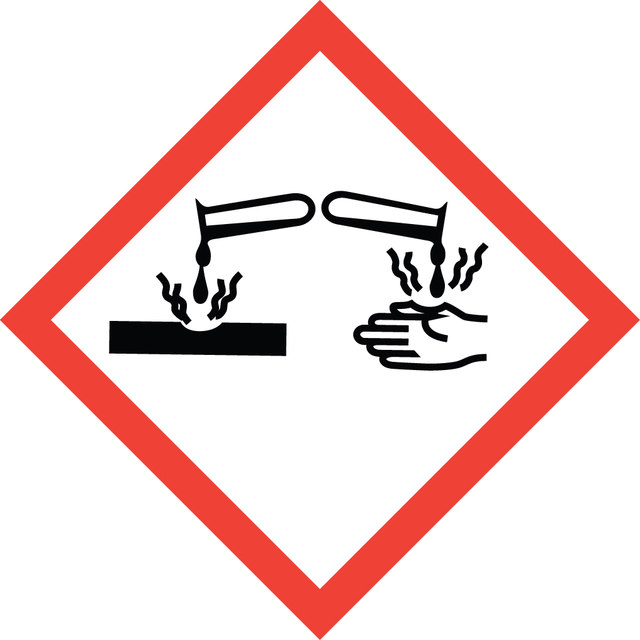
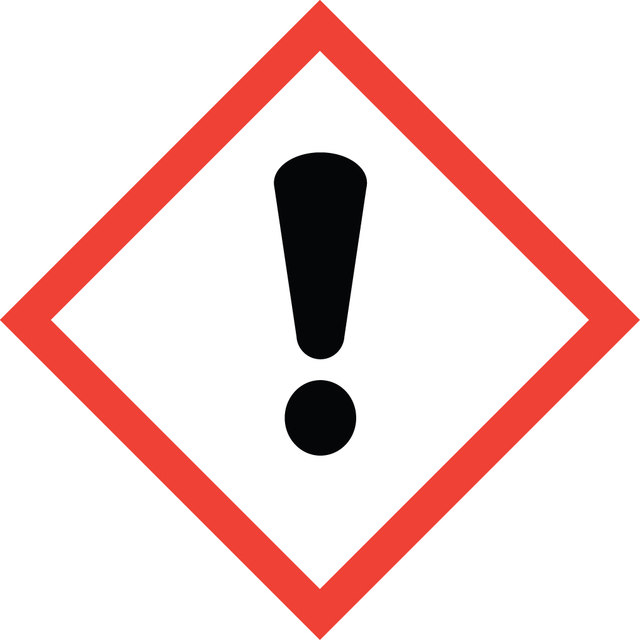
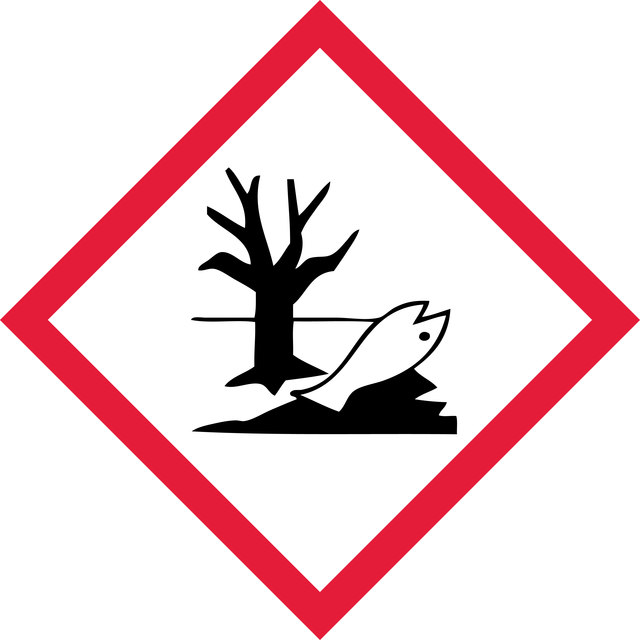
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1
Storage Class
13 - Non Combustible Solids
wgk_germany
WGK 3
flash_point_f
Not applicable
flash_point_c
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service