A6941
Alcohol Oxidase from Candida boidinii
lyophilized powder, 5-15 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
AOD1, AOX, Alcohol:oxygen oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(3)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
fungus (Candida boidinii)
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
5-15 units/mg protein
mol wt
octomer 600 kDa by sedimentation equilibrium
solubility
100 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.5: soluble 1.0 mg/mL at 25 °C (Cold)
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Alcohol Oxidase (AOX) is a homo-octamer composed of eight flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactors and belongs to the glucose-methanol-choline (GMC) family of oxidoreductases. The AOX1 and AOX2 genes are responsible for encoding AOX. Alcohol oxidase is primarily localized in the peroxisome but is also found in the cytoplasm. Alcohol oxidase is a 600 kDa homooctomeric flavoprotein with eight equal 74 kDa subunits; each containing a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) molecule.
Alcohol Oxidase (AOX) is a homo-octamer composed of eight flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) cofactors and belongs to the glucose-methanol-choline (GMC) family of oxidoreductases. The AOX1 and AOX2 genes are responsible for encoding AOX. Alcohol oxidase is primarily localized in the peroxisome but is also found in the cytoplasm. Alcohol oxidase is a 600 kDa homooctomeric flavoprotein with eight equal 74 kDa subunits; each containing a flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) molecule.
Application
Alcohol oxidase has been used:
- to catalyze the oxidation of short-chain, primary, aliphatic alcohols to their respective aldehydes .
- to study methanol metabolism in yeasts, such as Candida, Pichia, and Hansenula.
- to study protein translocation into peroxisomes.
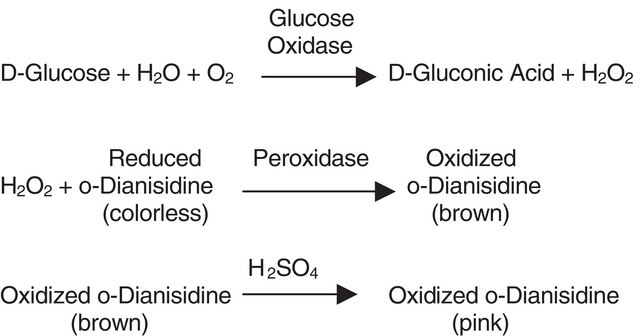
- for the determination of ethanol concentration in alcoholic drinks using enzymatic assay.
- in development of enzyme electrode for the determination of alcohols.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Alcohol oxidase has the highest affinity for methanol. The affinity decreases with increasing chain length of the alkyl (R) group. The enzyme shows little activity toward secondary, tertiary, or aromatic alcohols; or aliphatic alcohols with a chain length of more than 5 carbons. The pH range for activity of this product is 6.5-8.5, with the optimum pH being 7.5. Alcohol oxidases facilitate the conversion of alcohol into carbonyl compounds while producing hydrogen peroxide. It is also the first enzyme in the yeast methanol utilization pathway.
Unit Definition
One unit will oxidize 1.0 μmole of methanol to formaldehyde per min at pH 7.5 at 25 °C.
Physical form
Contains potassium phosphate buffer salts, DTE, and stabilizer
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service