SML1395
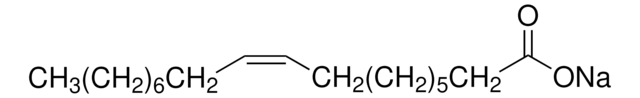
Arachidonic acid sodium salt
from Mortierella alpina, ≥98.5% (GC), waxy solid, lipid precursor
동의어(들):
5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid, Eicosa-5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z-tetraenoic acid, Sodium arachidonate, cis,cis,cis,cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic acid sodium salt, 20:4
로그인조직 및 계약 가격 보기
모든 사진(1)
About This Item
추천 제품
Product Name
Arachidonic acid sodium salt from Mortierella alpina, ≥98.5% (GC)
생물학적 소스
Mortierella alpina
Quality Level
분석
≥98.5% (GC)
양식
waxy solid
색상
white to off-white
solubility
methanol: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless to faintly yellow
배송 상태
dry ice
저장 온도
−20°C
SMILES string
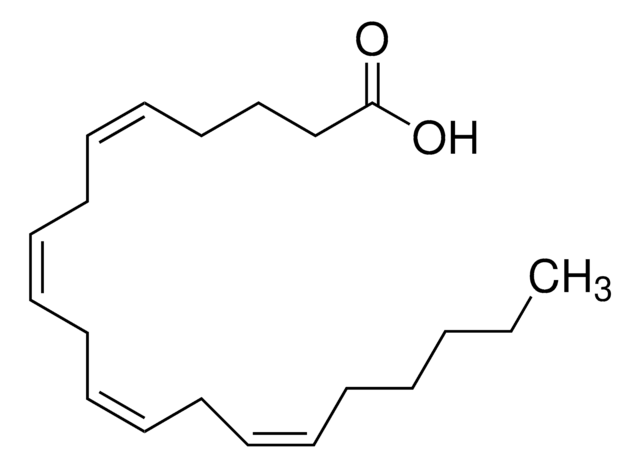
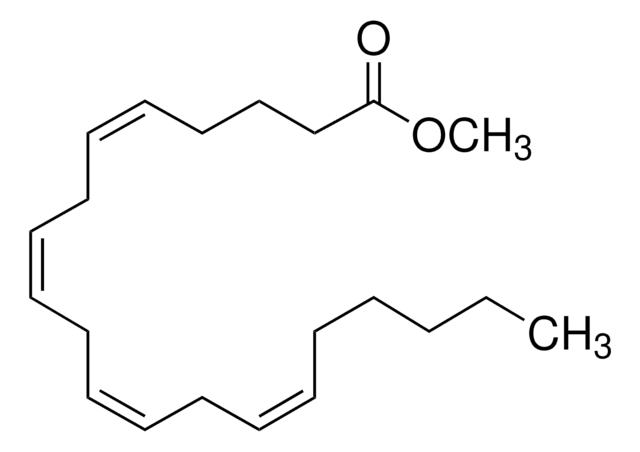
O=C(O[Na])CCC/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\C/C=C\CCCCC
InChI
1S/C20H32O2.Na/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-17-18-19-20(21)22;/h6-7,9-10,12-13,15-16H,2-5,8,11,14,17-19H2,1H3,(H,21,22);/q;+1/p-1/b7-6-,10-9-,13-12-,16-15-;
InChI key
DDMGAAYEUNWXSI-XVSDJDOKSA-M
관련 카테고리
일반 설명
Arachidonic acid (AA) is a polyunsaturated ϖ fatty acid constituent of the phospholipids of cell membranes. Structurally, it is a 20-carbon chain that contains four cis double bonds, which allow the free acid form of AA to be an insoluble oil; this can be converted to the water-soluble sodium salt form within the normal physiological pH range. Arachidonic acid is metabolized by multiple enzymes to yield various metabolites; AA and its metabolites play important roles in a variety of biological processes, including signal transduction, smooth muscle contraction, chemotaxis, cell proliferation and differentiation and apoptosis.
애플리케이션
Arachidonic acid is used in assays to measure activity of oxidizing enzymes, such as cyclooxygenase, as well as in assays to determine platelet inhibition in whole blood. Arachidonic acid has been demonstrated to bind to the a subunit of G protein and inhibit the activity of Ras GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs), to have a role in the development and progression of prostate cancer, and to enhance formation of lipid bodies in human mast cells.
생화학적/생리학적 작용
Arachidonic acid (ARA) is a vital component of biological cell membranes, providing them with the necessary fluidity and flexibility crucial for the functioning of all cells, particularly in the nervous system, skeletal muscle, and immune system. Free ARA regulates the activity of ion channels, various receptors, and enzymes, both through activation and inhibition. ARA undergoes reacylation/deacylation cycles within cell membranes, maintaining its concentration at a low level and restricting its availability for oxidation. Metabolites resulting from ARA oxidation do not initiate inflammation but contribute to it, and more significantly, they generate mediators crucial for resolving inflammation and promoting wound healing. Released arachidonic acid (AA) reacts with molecular oxygen nonenzymatically, through oxidative stress, and enzymatically through the action of oxygenase enzymes. AA is oxidized to prostaglandins and thromboxanes by at least two cyclooxygenase (COX) isoforms, to leukotrienes and lipoxins by lipoxygenases, and to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids via cytochrome p450-catalyzed metabolism. Cellular uptake of arachidonic acid is energy-dependent and involves protein-facilitated transport across the plasma membrane.
주의사항
The sodium salts of arachidonic acid are very sensitive to oxidation and will turn yellow and deteriorate rapidly in air. They are packaged under vacuum in sealed ampules. Once opened the product must be used quickly or transferred into an inert atmosphere (dry argon) as soon as possible.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point (°F)
235.4 °F - closed cup
Flash Point (°C)
113 °C - closed cup
이미 열람한 고객
자사의 과학자팀은 생명 과학, 재료 과학, 화학 합성, 크로마토그래피, 분석 및 기타 많은 영역을 포함한 모든 과학 분야에 경험이 있습니다..
고객지원팀으로 연락바랍니다.