C3515
Catalase from Aspergillus niger
ammonium sulfate suspension, ≥4,000 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
H2O2:H2O2 oxidoreductase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
eCl@ss:
32160410
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
Aspergillus niger
Quality Level
form
ammonium sulfate suspension
specific activity
≥4,000 units/mg protein
mol wt
tetramer ~250 kDa
storage condition
(Tightly closed)
technique(s)
FISH: suitable
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O(CC)C(=O)c1ccc(cc1)O
InChI
1S/C9H10O3/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6,10H,2H2,1H3
InChI key
NUVBSKCKDOMJSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
General description
Research area: Cell Signaling
Catalase is an active enzyme present in aerobic organisms. It is a ferric hemoprotein and a tetramer.
Catalase is an active enzyme present in aerobic organisms. It is a ferric hemoprotein and a tetramer.
Application
Catalase from Aspergillus niger has been used:
- as a positive control during the functional characterization of Clostridium difficile spore coat proteins.
- as a component of the catalase solution to prepare GLOX buffer with enzymes to maintain the embryos of Caenorhabditis elegans before single-molecule fluorescence in situ hybridization (smFISH) studies
- as a component of the imaging buffer for stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) imaging of platelet-rich plasma
- as a supplement in Todd Hewitt media plus 0.5 % yeast extract (THY) media for the neutralization of pneumococcal H2O2
Biochem/physiol Actions
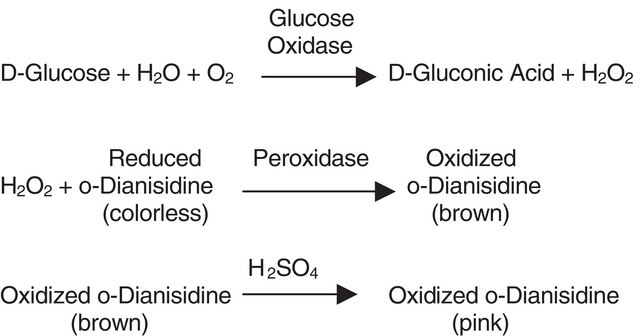
Catalase catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Each subunit of the tetramer contains iron bound to a protoheme IX group. The enzyme also strongly binds NADP, which is in close proximity to the heme group. Isoelectric point is found to be 6.5. Optimum pH for catalytic activity is 7.0. The enzyme activity is inhibited by 3-amino-1-H-1,2,4 triazole, cyanide, azide, hydroxylamine, cyanogen bromide, 2-mercaptoethanol, dithiothreitol, dianisidine, and nitrate. Incubation of catalase with ascorbate or ascorbate/Cu2+ results in degradation of the catalase molecule.
Catalase is involved in catalyzing the degradation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to water and free oxygen. Catalase is used commercially for decomposing H2O2 as it is added as an antimicrobial agent in process streams. It also catalyzes the oxidation of electron donors like ethanol and phenols during lower concentrations of H2O2. Catalase shows antioxidant activity by protecting cells from higher levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Increased expression of catalase is observed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, gastric cancer, glioma, and melanoma. Decreased levels of catalase are seen in acute myeloid leukemia, lung, pancreatic, prostate, and skin (non-melanoma) cancers. Hence catalase exhibits a dual role in cancer.
Caution
Freezing of solutions is not recommended.
Unit Definition
One unit will decompose 1.0 μmole of H2O2 per min at pH 7.0 at 25 °C, while the H2O2 concentration falls from 10.3 to 9.2 mM, measured by the rate of decrease of A240.
Physical form
Suspension in 3.2 M (NH4)2SO4 solution, pH 6.0
Analysis Note
Protein determined by biuret
antibody
Product No.
Description
Pricing
enzyme
Product No.
Description
Pricing
inhibitor
Product No.
Description
Pricing
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service